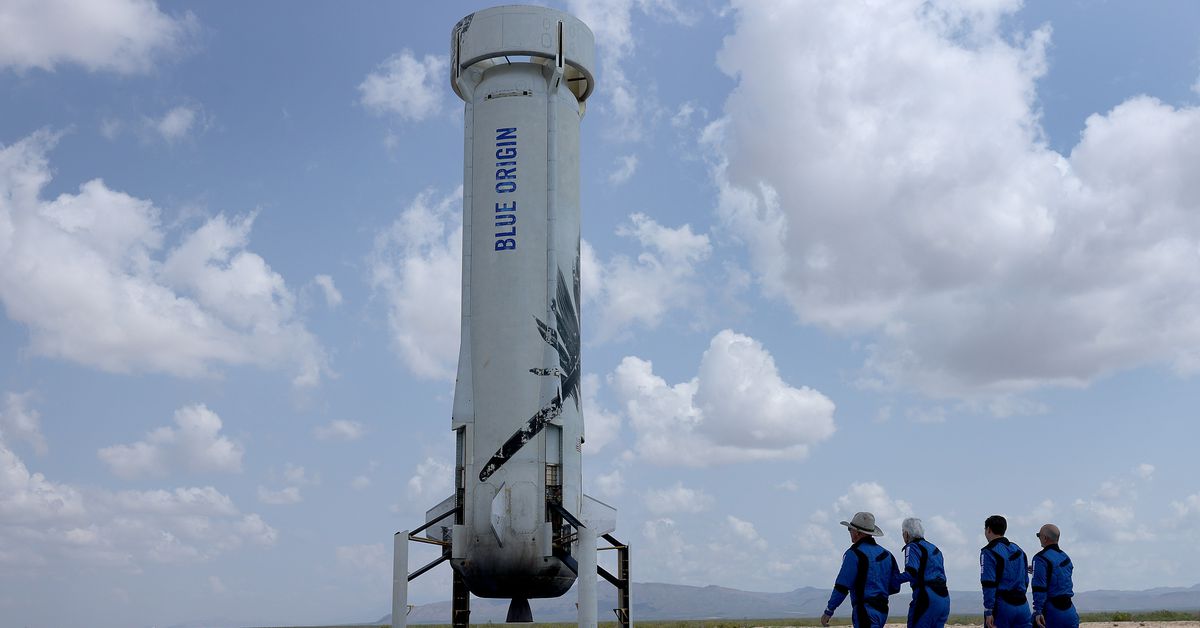
For many, the rise of commercial space tourism is a vulgar display of wealth and power. Amid several global crises, including climate change and a pandemic, billionaires are spending their cash on launching themselves into space for fun. When Amazon founder Jeff Bezos told reporters after his first space tourism trip on Tuesday that Amazon customers and employees had “paid” for his flight, that only intensified that criticism.
But critics won’t deter Bezos and the other superrich. Space tourism is now a reality for the people who can afford it — and it will have repercussions for everyone on Earth.
In fact, all signs indicate that the market for these trips is already big enough that they’ll keep happening. Jeff Bezos’s spaceflight company Blue Origin already has two more trips scheduled later this year, while Virgin Galactic, the space firm founded by billionaire Richard Branson, has at least 600 people who have already paid around $250,000 each for future tickets on its spaceplane.
Now, as the commercial space tourism market (literally) gets off the ground, there are big questions facing future space travelers — and everyone else on the planet. Here are answers to the six biggest ones.
1. What will people actually be able to see and experience on a space trip?
The biggest perk of traveling to space is the view. Just past the boundary between space and Earth, passengers can catch a stunning glimpse of our planet juxtaposed against the wide unknown of space. If a passenger is riding on a Virgin Galactic flight, they will get about 53 miles above sea level. Blue Origin riders will get a little bit higher, about 62 miles above sea level and past the Kármán line, the internationally recognized boundary between Earth and space. Overall, the experience on both flights is pretty similar.
The view is meant to be awe-inducing, and the experience even has its own name: the Overview Effect. “When you see Earth from that high up, it changes your perspective on things and how interconnected we are and how we squander that here on Earth,” Wendy Whitman Cobb, a professor at the US Air Force’s School of Advanced Air and Space Studies, told Recode.
Another perk of these trips is that space tourists will feel a few minutes of microgravity, which is when gravity feels extremely weak. That will give them the chance to bounce around a spacecraft weightlessly before heading back to Earth.
But Blue Origin’s and Virgin Galactic’s flights are relatively brief — about 10 and 90 minutes long, respectively. Other space tourism flights from SpaceX, the space company founded by Elon Musk, will have more to offer. This fall, billionaire Jared Isaacman, who founded the company Shift4 Payments, will pilot SpaceX’s first all-civilian flight, the Inspiration4, which will spend several days in orbit around Earth. In the coming years, the company has also planned private missions to the International Space Station, as well as a trip around the moon.
These trips are meant to be enjoyed by space nerds who longed to be astronauts. But there’s another reason rich people want to go to space: demonstrating exclusivity and conspicuous consumption. More than a few people can afford a trip to Venice or the Maldives. But how many people are privileged enough to take a trip to space?
“What a nice way of showing off these days than to post a picture on Instagram from space,” Sridhar Tayur, a Carnegie Mellon business professor, told Recode.
2. Does commercial space travel have any scientific goals, or is it really just a joyride?
Right now, space tourism flights from Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin have only reached suborbital space, which means that flights enter space but do not enter orbit around Earth. Scientifically, that’s not a new frontier. Though these current flights use new technology, suborbital flight with humans aboard was accomplished by NASA back in the early 1960s, Matthew Hersch, a historian of technology at Harvard, told Recode.
Right now, it’s not clear these trips will offer scientists major new insights, but they might provide information that could be used in the future for space exploration. In fact, these trips are also being marketed as potential opportunities for scientific experiments. For instance, the most recent Virgin Galactic flight carried plants and tested how they responded to microgravity.
These private companies primarily see opportunities in their commercial vehicles that can be reused at scale, which will allow the same rockets (or in Virgin Galactic’s case, spaceplanes) to go to space again and again, which lowers the overall cost of space tourism.
Billionaires and their private space companies also see the development of these rockets as an opportunity to prepare for flights that will do even more, and go even farther, into space. Bezos, for instance, has argued that New Shepard’s suborbital flights will help prepare the company’s future missions, including its New Glenn rocket, which is meant for orbital space.
“The fact of the matter is, the architecture and the technology we have chosen is complete overkill for a suborbital tourism mission,” Bezos said at Tuesday’s post-launch briefing. “We have chosen the vertical landing architecture. Why did we do that? Because it scales.”
Beyond potential scientific advancements in the future, suborbital spaceflight might also create new ways to travel from one place on earth to another. SpaceX, for instance, has advertised that long-haul flights could be shortened to just 30 minutes by traveling through space.
3. Is it safe?
Right now, it’s not entirely clear just how risky space tourism is.
One way space tourism companies are trying to keep travelers safe is by requiring training so that the people who are taking a brief sojourn off Earth are as prepared as possible.
On the flight, people can experience intense altitude and G-forces. “This is sustained G-forces on your body, upwards of what can be 6 G in one direction — which is six times your body weight for upwards of 20 or 30 seconds,” Glenn King, the chief operating officer of the Nastar Center — the aerospace physiology training center that prepared Richard Branson for his flights — told Recode. “That’s a long time when you have six people, or your weight, pressing down on you.”
There’s also the chance that space tourists will be exposed to radiation, though that risk depends on how long you’re in space. “It’s a risk, especially more for the orbital flight than sub-orbital,” explains Whitman Cobb. “Going up in an airplane exposes you to a higher amount of radiation than you would get here on the ground.” She also warns that some tourists will likely barf on the ride.
There doesn’t seem to be an age limit on who can travel, though. The most recent Blue Origin flight included both the youngest person to ever travel to space, an 18-year-old Dutch teenager, as well as the oldest: 82-year-old pilot Wally Funk.
4. How much will tickets cost?
The leaders in commercial space tourism already claim they have a market to support the industry. While Bezos hinted on Tuesday the price would eventually come down — as eventually happened with the high prices of the nascent airline industry — for now, ticket prices are in the low hundreds of thousands, at least for Virgin Galactic. That price point would keep spaceflight out of reach for most of humanity, but there are enough interested rich people that space tourism seems to be economically feasible.
“If you bring it down to $250,000, the wait times [to buy a ticket] will be very long,” Tayur, of Carnegie Mellon, told Recode.
5. What impact will commercial space travel have on the environment?
The emissions of a flight to space can be worse than those of a typical airplane flight because just a few people hop aboard one of these flights, so the emissions per passenger are much higher. That pollution could become much worse if space tourism becomes more popular. Virgin Galactic alone eventually aims to launch 400 of these flights annually.
“The carbon footprint of launching yourself into space in one of these rockets is incredibly high, close to about 100 times higher than if you took a long-haul flight,” Eloise Marais, a physical geography professor at the University College London, told Recode. “It’s incredibly problematic if we want to be environmentally conscious and consider our carbon footprint.”
These flights’ effects on the environment will differ depending on factors like the fuel they use, the energy required to manufacture that fuel, and where they’re headed — and all these factors make it difficult to model their environmental impact. For instance, Jeff Bezos has argued that the liquid hydrogen and oxygen fuel Blue Origin uses is less damaging to the environment than the other space competitors (technically, his flight didn’t release carbon dioxide), but experts told Recode it could still have significant environmental effects.
There are also other risks we need to keep studying, including the release of soot that could hurt the stratosphere and the ozone. A study from 2010 found that the soot released by 1,000 space tourism flights could warm Antarctica by nearly 1 degree Celsius. “There are some risks that are unknown,” Paul Peeters, a tourism sustainability professor at the Breda University of Applied Sciences, told Recode. “We should do much more work to assess those risks and make sure that they do not occur or to alleviate them somehow — before you start this space tourism business.” Overall, he thinks the environmental costs are reason enough not to take such a trip.
6. Who is regulating commercial space travel?
Right now, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has generally been given the job of overseeing the commercial space industry. But regulation of space is still relatively meager.
One of the biggest areas of concern is licensing launches and making sure that space flights don’t end up hitting all the other flying vehicles humans launch into the sky, like planes and drones. Just this June, a SpaceX flight was held up after a helicopter flew into the zone of the launch.
There’s a lot that still needs to be worked out, especially as there are more of these launches. On Thursday, the Senate hosted a hearing with leaders of the commercial space industry focused on overseeing the growing amount of civil space traffic.
At the same time, the FAA is also overseeing a surging number of spaceports — essentially airports for spaceflight — and making sure there’s enough space for them to safely set up their launches.
But there are other areas where the government could step in. “I think the cybersecurity aspect will also play a very vital role, so that people don’t get hacked,” Tayur said. The FAA told Recode that the agency has participated in developing national principles for space cybersecurity, but Congress hasn’t given it a specific role in looking at the cybersecurity of space.
At some point, the government might also step in to regulate the environmental impact of these flights, too, but that’s not something the FAA currently has jurisdiction over.
In the meantime, no government agency is currently vetting these companies when it comes to the safety of the human passengers aboard. An FAA official confirmed with Recode that while the agency is awarding licenses to companies to carry humans to space, they’re not actually confirming that these trips are safe. That’s jurisdiction Congress won’t give the agency until 2023.
There doesn’t seem to be an abundance of travelers’ insurance policies for space. “Passengers basically sign that they’re waiving all their rights,” Whitman Cobb said. “You’re acknowledging that risk and doing it yourself right now.”
So fair warning, if you decide to shell out hundreds of thousands of dollars for a joyride to space: You’d likely have to accept all responsibility if you get hurt.