Uncategorized
<!–
–>
Managing data in Shopify can get tedious fast, especially when you’re dealing with bulk updates, vendor-supplied files, or inconsistent formatting. That’s where the new Data Transformation feature in the Improved Import & Export app for Shopify comes in. It lets you automate changes to your import data on the fly using simple, secure PHP scripts.
Whether you need to increase prices by 20%, normalize tag formatting, or adjust inventory levels based on specific rules, this new feature gives you full control, directly within the import process. Instead of manually editing spreadsheets or running post-import corrections, you can now apply logic at the source using a powerful $row scripting environment. And thanks to a strict PHP function whitelist, your transformations remain safe, stable, and lightning fast.
In this article, we’ll walk you through how Shopify data transformation works, which functions you can use, and real-world examples that make imports smarter, not harder.

Table of contents
- What Is Shopify PHP Data Transformation on Imports?
- How the Shopify PHP Script Editor Works
- List of Allowed PHP Functions
- Use Cases and Practical Examples for Shopify PHP Data Transformation
- Final Thoughts: Reduce CSV Editing with Shopify PHP Data Transformation
- FAQ: Shopify PHP Data Transformation
What Is Shopify PHP Data Transformation on Imports?
Data Transformation in the context of Shopify imports refers to the ability to automatically modify product data as it’s being imported, without changing the source file. This is done through a built-in scripting editor available in the Improved Import & Export app for Shopify. Instead of editing your CSV or Excel files manually before upload, you can now define rules and logic that adjust the data row by row during the import process.
This feature is especially useful when you’re importing large datasets or files from external vendors, suppliers, or marketplaces. Inconsistent formats, missing values, or non-standard conventions can all be handled on the fly, saving time and reducing human error. From bulk price increases and inventory adjustments to SEO tweaks and field cleanup, data transformation enables you to automate routine changes and ensure data accuracy across your catalog.
How the Shopify PHP Script Editor Works
At the core of this feature is the $row variable — a PHP associative array representing a single row of your import file. You can use $row[‘Field Name’] to access or modify individual fields, such as Variant Price, Tags, Vendor, or any custom metafield.
The script editor is available right at the first step of the import process in the Improved Import & Export app for Shopify. When setting up a new import profile or running a manual import, you’ll see a “Data modification” feature in the General settings. Activate it to display the “PHP Data Modification Script” window.
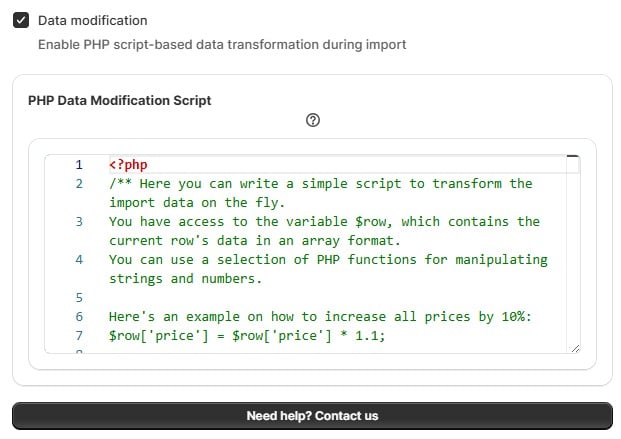
Here, you can input custom PHP code that manipulates each row of your import file as it’s processed. This happens before the data is sent to Shopify, allowing you to clean, calculate, or enrich values on the fly.
The scripting environment uses inline PHP code. You don’t need to define a full PHP file — just write your logic using the provided $row variable. Each row from your file is passed into this variable as an associative array, where each key corresponds to a column header (Note that it can be any header standard for Shopify, such as ‘Variant Price’, ‘Tags’, and ‘Inventory_#Paris Warehouse’or any third-party name). You simply write conditional statements, string manipulations, or mathematical operations to update the row fields as needed.
To maintain performance and security, the editor only supports a whitelisted set of PHP functions. These include common string, math, array, and date/time functions — like strtolower(), round(), explode(), or strtotime() — that are safe to execute during an import. Any non-whitelisted or risky functions will be blocked to prevent misuse or server instability. You can find the full list in the corresponding section below.
🚫 Important: Never overwrite the $row variable entirely. For example, avoid statements like $row = “test” or $row = []. Doing so will break the import process. Instead, always update specific keys within the $row array, like $row[‘title’] = ucfirst($row[‘title’]);.
List of Allowed PHP Functions
Below is a categorized list of all the PHP functions currently supported in Shopify import transformations. Use these to clean, format, calculate, or re-structure your data row by row — all within a safe and controlled environment.
| Function Group | Functions |
| String Functions | strlen, strpos, strtolower, strtoupper, trim, substr, str_replace, explode, implode, htmlspecialchars, ucfirst, lcfirst |
| Hashing Functions | md5, sha |
| Array Functions | in_array, count |
| Math Functions | abs, round, ceil, floor, max, min, rand, sqrt, pow |
| Date/Time Functions | time, date, strtotime, mktime |
| Variable Handling | isset, empty |
| JSON Functions | json_encode, json_decode |
| Multibyte String Functions | mb_* (see full list above) |
When to Use Multibyte String Functions
Multibyte string functions — those that start with mb_, like mb_strtolower() or mb_substr() — are designed to work with UTF-8 and other multibyte character encodings. Unlike standard string functions (e.g., strlen, substr), which operate byte-by-byte, multibyte functions operate character-by-character. This distinction is crucial when working with non-English alphabets, emojis, or accented characters.
Use multibyte string functions when:
- 🔤 Your import data includes non-Latin characters — such as German umlauts (ä, ö, ü), Japanese kana (カタカナ), Chinese characters (汉字), Arabic letters (ع), or accented French/Spanish text.
- 🧠 You need precise string handling in UTF-8 encoded files, especially when measuring string length, converting to upper/lowercase, or extracting substrings.
- 🌍 You’re managing a multilingual Shopify store and transforming product titles, tags, descriptions, or metafields that contain international text.
🔧 Example:
$row[‘title’] = mb_strtoupper($row[‘title’]);
This will convert all characters, including é, ü, or ñ — something strtoupper() would fail to handle accurately.
Pro tip: When in doubt, default to mb_ functions if you know your import file contains non-English text. They’ll give you safer, cleaner results with better compatibility for global storefronts.
Use Cases and Practical Examples for Shopify PHP Data Transformation
Once you understand how the $row scripting environment works, you can unlock a powerful range of use cases for cleaning, transforming, and optimizing your Shopify product data. Below, you will find some practical examples to help you get started.
🔼 Increase Prices by a Percentage
Need to apply a markup to incoming prices from a supplier? This script checks whether the Variant Price field exists and whether its value is over 100. If so, it increases the price by 20% and rounds the result to two decimal places for currency precision.
if (isset($row[‘Variant Price’]) && $row[‘Variant Price’] > 100) {
$row[‘Variant Price’] = round($row[‘Variant Price’] * 1.2, 2);
}
📌 Why use it?
Ideal for stores that import product catalogs with cost prices or wholesale pricing and need to apply a markup automatically during import.
🧹 Clean Up Vendor Names and Tags
Vendor names or tags coming from third-party suppliers can be inconsistent with extra symbols, casing issues, or unwanted spaces. Here’s how to clean them up:
// Remove $ symbol from vendor name
$row[‘vendor’] = str_replace(‘$’, ”, $row[‘vendor’]);
// Convert tags to lowercase
$row[‘Tags’] = mb_strtolower($row[‘Tags’]);
📌 Why use it?
Keeps your store data clean and standardized, improving filter performance, tag-based merchandising, and SEO.
📦 Adjust Inventory Levels Automatically
Set default stock quantities if the imported file lists them as zero. This script ensures both general and warehouse-specific stock values are corrected:
if (isset($row[‘Variant Inventory Qty’]) && $row[‘Variant Inventory Qty’] == 0) {
$row[‘Variant Inventory Qty’] = ’99’;
}
if (isset($row[‘Inventory_#Paris Warehouse’]) && $row[‘Inventory_#Paris Warehouse’] == 0) {
$row[‘Inventory_#Paris Warehouse’] = ’99’;
}
📌 Why use it?
Prevents out-of-stock issues or placeholder values from affecting product availability in your Shopify storefront or connected sales channels.
🏷️ Generate SEO Titles or Metafields
Want to enhance your product SEO by dynamically generating meta titles? Combine fields like product title and product_type:
$row[‘metafields.seo.meta_title’] = $row[‘title’] . ‘ – ‘ . $row[‘product_type’];
📌 Why use it?
Reduces the need for post-import SEO optimization and ensures consistency across your store’s metadata.
🧠 Understanding How These PHP Scripts Work
All these scripts rely on the $row variable — an associative array that represents each row of your import file. Here’s a quick guide to working with it:
1. Accessing Row Data
You access each field by its column name in square brackets:
$productTitle = $row[‘title’];
2. Modifying Row Data
You can directly overwrite a field’s value like this:
$row[‘vendor’] = str_replace(‘$’, ”, $row[‘vendor’]);
3. Using Allowed PHP Functions
Only whitelisted PHP functions are allowed in the script editor. These include:
- String functions: strtolower, str_replace, trim, etc.
- Math functions: round, abs, ceil
- Array and variable handlers: isset, count, in_array
- Multibyte string functions like mb_strtolower for non-English characters
Example:
$row[‘Tags’] = mb_strtolower($row[‘Tags’]);
4. Conditionally Modifying Data
You can use if conditions to check values before modifying them. For example:
if (isset($row[‘Variant Inventory Qty’]) && $row[‘Variant Inventory Qty’] == 0) {
$row[‘Variant Inventory Qty’] = ’99’;
}
5. Performing Calculations
You can use mathematical operations to update numeric fields:
if (isset($row[‘Variant Price’]) && $row[‘Variant Price’] > 100) {
$row[‘Variant Price’] = round($row[‘Variant Price’] * 1.2, 2);
}
6. No Need to Return the Row
You do not need to use a return statement. Since $row is passed by reference, all changes you make are applied automatically during the import process.
These examples are just the beginning — once you understand how to manipulate $row, you can build sophisticated logic to match your store’s unique pricing, inventory, and SEO workflows.
To get help with scripts tailored to your specific business cases, contact our support
Final Thoughts: Reduce CSV Editing with Shopify PHP Data Transformation
The Data Transformation feature in the Improved Import & Export app for Shopify empowers merchants to take full control of their product data, right at the point of import. By using simple, secure PHP scripts, you can clean up messy vendor files, adjust prices or stock values in bulk, and generate SEO-optimized fields — all without touching your source file or performing post-import edits.
The benefits are clear:
✅ Clean, consistent data across your entire catalog
✅ Significant time savings through automation
✅ Fewer manual corrections and less room for human error
Whether you’re scaling your catalog, managing supplier feeds, or just want to streamline your workflow, this feature gives you the flexibility to tailor your data to your store’s exact needs.
🔧 Try it in your next Shopify import and experience the difference intelligent scripting can make.
👉 Explore the Improved Import & Export app for Shopify
📘 Read the full user manual
FAQ: Shopify PHP Data Transformation
How does the $row variable work in Shopify import scripts?
The $row variable represents a single row from your import file as an associative array. Each key corresponds to a column name in your CSV or Excel file. You can access and modify field values using this variable — for example, $row[‘price’] = $row[‘price’] * 1.1; increases the price by 10%.
Where can I find the script editor in the import process?
The script editor is available in Step 1 of the import setup within the Improved Import & Export app for Shopify. Look for the section labeled “PHP Data Modification Script.” Enable the Data modification checkbox to activate the editor, then write your PHP code directly in the input area.
What kind of PHP functions can I use in my transformation scripts?
Only a whitelisted set of secure PHP functions is allowed. These include commonly used string functions (strtolower, str_replace, trim), math functions (round, abs), array functions (count, in_array), date/time operations (strtotime, date), and multibyte string functions (mb_strtolower, etc.) for multilingual compatibility.
Can I use conditional logic in my import scripts?
Yes, you can use if statements and conditions to apply changes only when needed. For example, you might increase the price only if it’s above 100, or set inventory to 99 only when it’s currently 0.
Do I need to return the $row variable at the end of the script?
No return is necessary. The $row variable is passed by reference, so any changes you make to individual fields are automatically applied during the import. However, avoid overwriting the entire $row variable — doing so will break the script.
What happens if I use a non-whitelisted PHP function in my script?
The import will fail, and an error message will point out the disallowed function. To ensure successful data transformation, stick to the approved list of PHP functions supported by the app’s secure scripting environment.

Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.