Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the latest version of the popular web analytics platform that offers many new features and capabilities for online marketers and website owners. However, GA4 also comes with some challenges and changes that require careful attention and interpretation. One of the most important aspects of GA4 reporting and analysis is report thresholding in Google Analytics 4. Report thresholding is a feature that withholds certain data from reports and explorations to protect user privacy. This feature is new to GA4 and was not present in previous versions, such as Universal Analytics.
Report thresholding can affect the accuracy and completeness of your GA4 data and reports, especially if you have low-traffic or niche segments. Therefore, it is essential to understand how report thresholding works in GA4 and how to avoid it as much as possible.
In this blog post, we will explain what report thresholding is in GA4, why it is applied, when it is applied, how it affects your data and reports, and how you can minimize its impact on your GA4 reporting and analysis.
What is Report Thresholding in Google Analytics 4(GA4)?
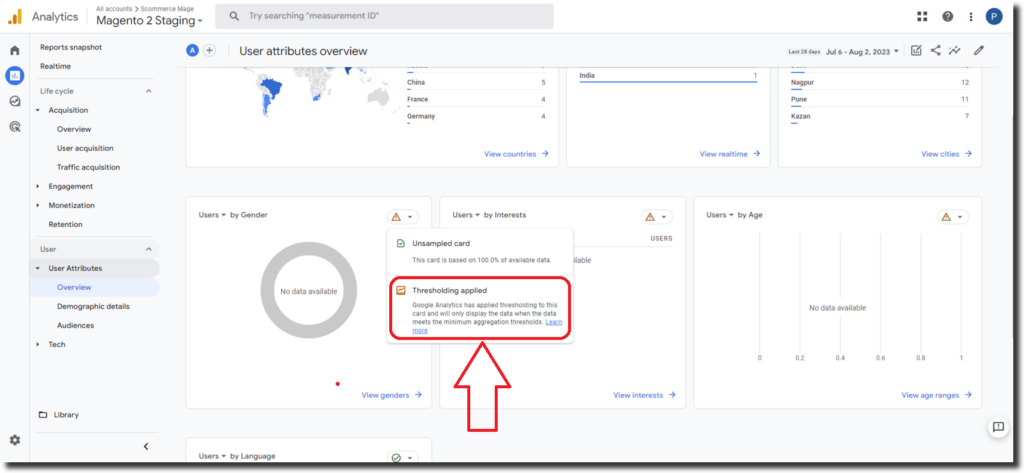
Report thresholding in GA4 is a feature that removes rows with very small numbers of users or events from reports and explorations to prevent the identification of individual users based on their data in GA4 reports.
For example, if you have a report that shows the number of users by country, and there is only one user from a certain country, that row will be removed from the report to protect the privacy of that user. Similarly, if you have an exploration that shows the number of events by event name, and there is only one event with a certain name, that row will be removed from the exploration to protect the privacy of the user who triggered that event.
Report thresholding is applied by GA4 automatically and cannot be adjusted by users. It is applied to all reports and explorations in GA4, regardless of the data source or date range.
Why is Report Thresholding Applied in Google Analytics 4(GA4)?
Report thresholding is applied in GA4 to comply with the privacy regulations and policies that govern the collection and processing of user data. These regulations and policies include:
• The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union
• The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in California
• The Google Analytics Terms of Service
• The Google Privacy Policy
These regulations and policies require that GA4 respects the privacy rights of users and does not collect or process any personally identifiable information (PII) or sensitive information without their consent. PII or sensitive information includes any data that can be used to identify or contact a specific individual, such as name, email address, phone number, etc.
However, even if GA4 does not collect or process any PII or sensitive information directly, it may still be possible to infer the identity of individual users based on other data points that are collected or processed by GA4, such as demographics, interests, behaviors, etc. For example, if a user has a very unique combination of attributes or actions that are recorded by GA4, such as age, gender, location, device type, event name, etc., it may be possible to identify that user by looking at their data in GA4 reports.
To prevent this possibility and protect user privacy, GA4 applies report thresholding to remove any rows with very small numbers of users or events from reports and explorations. This way, GA4 ensures that no individual user can be singled out or identified based on their data in GA4 reports.
When is Report Thresholding Applied in Google Analytics 4(GA4)?
Report thresholding is applied in GA4 when all of the following conditions are met:
• The report or exploration contains user counts or event counts as metrics
• The report or exploration contains dimensions or filters that can potentially identify individual users based on their data
• The report or exploration has low user counts or event counts in the specified date range
For example, report thresholding will be applied if you have a report that shows the number of users by age group and gender (user counts as metrics), and you filter by a specific country (dimension or filter that can potentially identify individual users), and you have less than 10 users from that country in the last 30 days (low user count in the specified date range).
However, report thresholding will not be applied if you have a report that shows the number of sessions by device category (session counts as metrics), and you filter by a specific country (dimension or filter that can potentially identify individual users), and you have more than 10 sessions from that country in the last 30 days (high session count in the specified date range).
How Does Report Thresholding Affect Your Data and Reports in GA4?
Report thresholding can affect your data and reports in GA4 in various ways, depending on the type and level of thresholding that is applied. There are two types of thresholding that can be applied in GA4:
- Row-level thresholding: This type of thresholding removes entire rows from reports and explorations if they have very small numbers of users or events. For example, if you have a report that shows the number of users by country, and there is only one user from a certain country, that row will be removed from the report.
- Cell-level thresholding: This type of thresholding replaces the values of certain cells in reports and explorations with “<10” if they have very small numbers of users or events. For example, if you have a report that shows the number of users by age group and gender, and there are only two female users in the 18-24 age group, the value of that cell will be replaced with “<10” in the report.
The level of thresholding that is applied in GA4 depends on the reporting identity that is used by your GA4 property.
What is Reporting Identity?
Reporting identity is the method Analytics uses to identify your users. The reporting identity is the identity space or spaces that GA4 uses to measure users across devices and platforms.
. There are four identity spaces that GA4 can use:
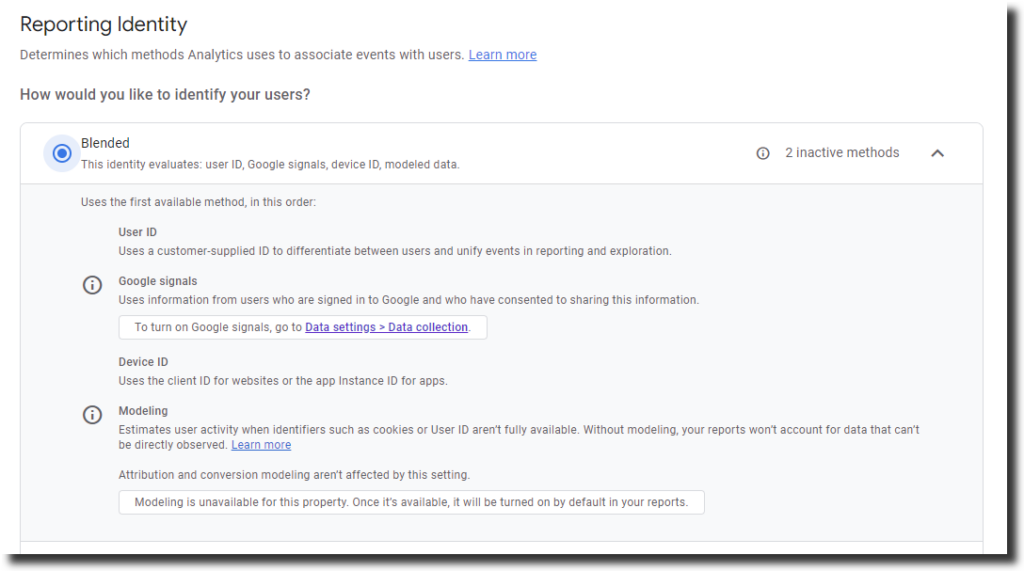
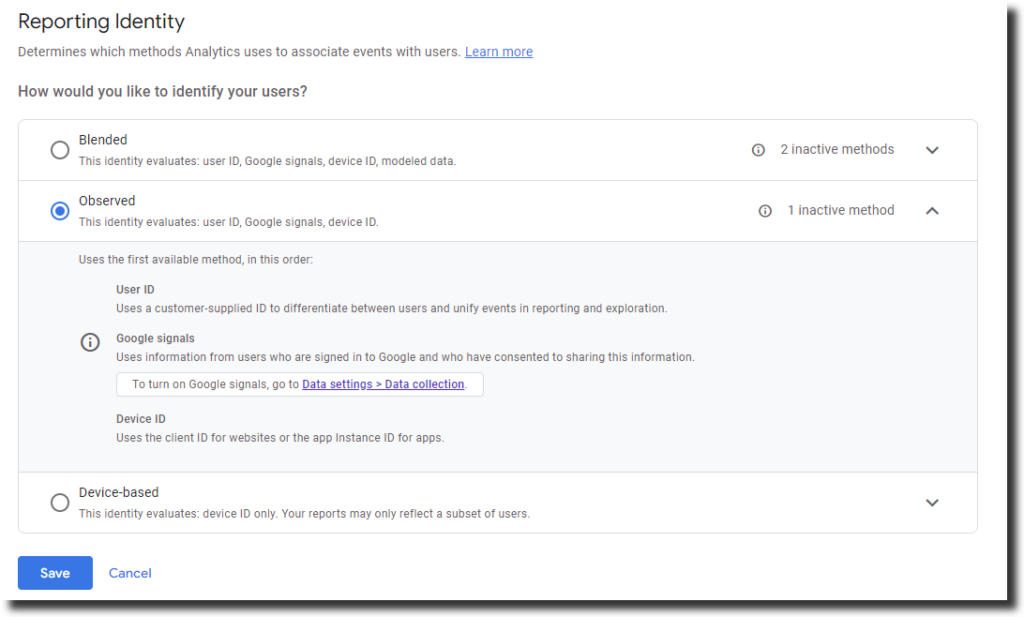
- User ID: This is a custom identifier that you assign to your signed-in users and send to GA4 along with your data. This is the most accurate identity space, as it uses your own data to identify your users.
- Google signals: This is data from users who are signed in to Google and have consented to share their information. This identity space allows GA4 to associate data from different devices and platforms using Google accounts.
- Device ID: This is an identifier that GA4 assigns to each device or browser that visits your website or app. This identity space uses cookies or app instance IDs to identify your users.
- Modeling: This is a method that GA4 uses to fill in the gaps when users decline Analytics identifiers like cookies. This identity space uses the data of similar users who accept cookies to model the behavior of those who decline cookies.
How to Set Up Reporting Identity in GA4?
To set your preferences for default reporting identity in Google Analytics 4, follow these steps:
- Log into your GA4 property and click “Admin” on the bottom left.
- Under “Property,” click “Default reporting identity.”
- Select between “Blended”, “Observed”, or “Device Based”
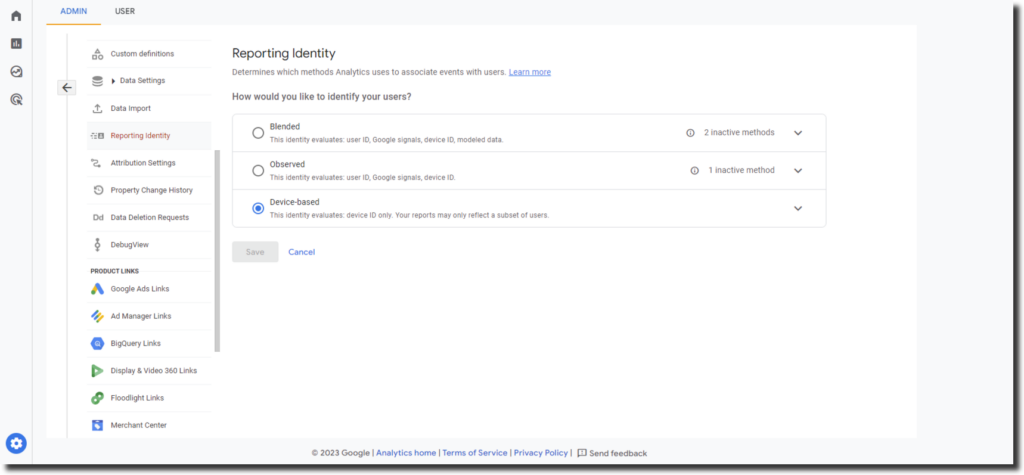
- Blended: This option uses a combination of User ID, Google signals, Device ID, and Modeled data if nothing else is available. This option provides the most comprehensive and holistic view of user behavior, but it also requires more configuration and consent from users.
- Observed: This option uses User ID if available, followed by Google signals if enabled, and then Device ID. This option is similar to Blended, but it does not use Modeled data to fill in the gaps when user data cannot be observed. This option may provide more accurate data, but it may also result in lower user counts.
- Device-based: This option uses Device ID as the identifier. This option is the simplest and default one, but it may not capture cross-device or cross-platform user behavior. This option may result in higher user counts, but lower engagement metrics.
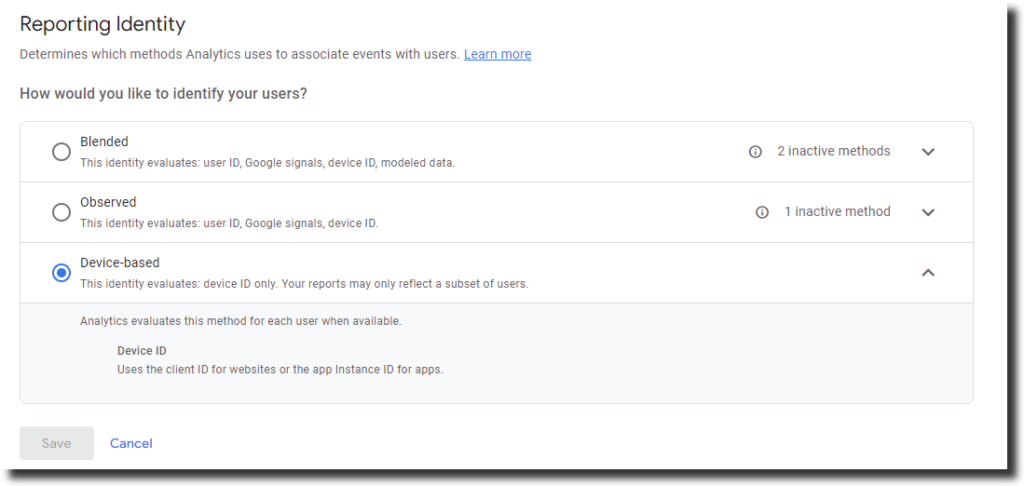
You can select one of these reporting identity options in GA4 by clicking Admin, then Reporting Identity in the Property column. The choice of reporting identity depends on your business goals and data needs. You can also compare different reporting identities using the Identity Explorer report in GA4
Depending on which reporting identity option you choose for your GA4 property, you may see different levels of thresholding applied to your data and reports in GA4. For example, if you choose blended as your reporting identity option, you may see more rows or cells removed or replaced with “<10” than if you choose by device ID only or by User-ID only.
How to Avoid Report Thresholding in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)?
Report thresholding is applied by GA4 automatically and cannot be adjusted by users. However, there are some ways to avoid or minimize report thresholding in GA4 as much as possible. Here are some tips and tricks on how to avoid report thresholding in GA4:
- Choose a reporting identity option that suits your needs and preferences. If you want to see the most comprehensive view of your users across devices and platforms, you may have to accept some level of thresholding by choosing blended as your reporting identity option. However, if you want to see a simpler or more accurate view of your users based on their devices or browsers or your own data, you may be able to avoid or reduce thresholding by choosing by device ID only or by User-ID only as your reporting identity option.
- Implement User-ID for signed-in users. If you have signed-in users on your website or app, you can implement User-ID to assign them custom identifiers and send them to GA4 along with your data. User-ID is the most accurate identity space, as it uses your own data to identify your users. User-ID also applies no thresholding at all, so you can see all the data for your signed-in users without any removals or replacements.
- Activate Google signals for cross-device tracking. If you want to track your users across different devices and platforms using Google accounts, you can activate Google signals for your GA4 property. Google Signals is an identity space that allows GA4 to associate data from different devices and platforms using Google accounts. Google signals also applies less thresholding than device ID or modeling, so you can see more data for your cross-device users without too many removals or replacements.
- Expand the date range for your reports and explorations. Report thresholding is applied when you have low user counts or event counts in the specified date range. If you have a narrow date range, such as a single day or week, you may have more rows or cells removed or replaced with “<10” than if you have a wider date range, such as a month or year. Expanding the date range may increase the number of users or events that are included in your reports and explorations, enabling you to see more data without any thresholding.
- Use dimensions and filters that are less likely to identify individual users. Report thresholding is applied when you have dimensions or filters that can potentially identify individual users based on their data. If you use dimensions or filters that are very specific or unique, such as age group, gender, location, device type, event name, etc., you may have more rows or cells removed or replaced with “<10” than if you use dimensions or filters that are more general or common, such as channel, medium, source, etc. Using dimensions and filters that are less likely to identify individual users may reduce the chances of thresholding being applied to your reports and explorations.
- Use metrics that are not based on user counts or event counts. Report thresholding is applied when you have user counts or event counts as metrics. If you use metrics that are based on user counts or event counts, such as users, new users, sessions per user, events per user, etc., you may have more rows or cells removed or replaced with “<10” than if you use metrics that are not based on user counts or event counts, such as sessions, page views, bounce rate, conversion rate, etc. Using metrics that are not based on user counts or event counts may avoid thresholding being applied to your reports and explorations.
Conclusion
Report thresholding is a feature that withholds certain data from reports and explorations in GA4 to protect user privacy. Report thresholding can affect the accuracy and completeness of your GA4 data and reports, especially if you have low-traffic or niche segments.
To understand and avoid report thresholding in GA4, you need to know how it works, why it is applied, when it is applied, how it affects your data and reports, and how you can minimize its impact on your GA4 reporting and analysis.
We hope this blog post has helped you understand what report thresholding is in GA4 and how to avoid it as much as possible. If you have any questions or need any assistance with your GA4 implementation or reporting, feel free to contact us. We are happy to help you with your GA4 project. You can also check out our fully working Extension that implements GA4 setup through GTM.






