The letter, which was organized by the Stanford University microbiologist David Relman and the University of Washington virologist Jesse Bloom, takes aim at a recent joint study of covid origins undertaken by the World Health Organization and China, which concluded that a bat virus likely reached humans via an intermediate animal and that a lab accident was “extremely unlikely.”
That conclusion was not scientifically justified, according to the authors of the new letter, since no trace of how the virus first jumped to humans has been found and the possibility of a laboratory accident received only a cursory look. Just a handful of the 313 pages of the WHO origins report and its annexes are devoted to the subject.
Marc Lipsitch, a well-known Harvard University epidemiologist who is among the signers of the letter, said he had not expressed a view on the origin of the virus until recently, choosing instead to focus on improving the design of epidemiological studies and vaccine trials—in part because the debate over the lab theory has become so controversial. “I stayed out of it because I was busy dealing with the outcome of the pandemic instead of the origin,” he says. “[But] when the WHO comes out with a report that makes a specious claim about an important topic … it’s worth speaking out.”
Several of those signing the letter, including Lipsitch and Relman, have in the past called for greater scrutiny of “gain of function” research, in which viruses are genetically modified to make them more infectious or virulent. Experiments to engineer pathogens were also ongoing at the Wuhan Institute of Virology, China’s leading center for studying bat viruses similar to SARS-CoV-2. Some see the fact that covid-19 first appeared in the same city in which the lab is located as circumstantial evidence that a laboratory accident could be to blame.
Lipsitch has previously estimated the risk of a pandemic caused by accidental release from a high-security biolab at between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 per year, and he has warned that the proliferation of thousands of such labs around the globe is a major concern.
Even though Chinese scientists have said no such leak occurred in this case, the letter writers say that can only be established through a more independent investigation. “A proper investigation should be transparent, objective, data-driven, inclusive of broad expertise, subject to independent oversight, and responsibly managed to minimize the impact of conflicts of interest,” they write. “Public health agencies and research laboratories alike need to open their records to the public. Investigators should document the veracity and provenance of data from which analyses are conducted and conclusions drawn.”
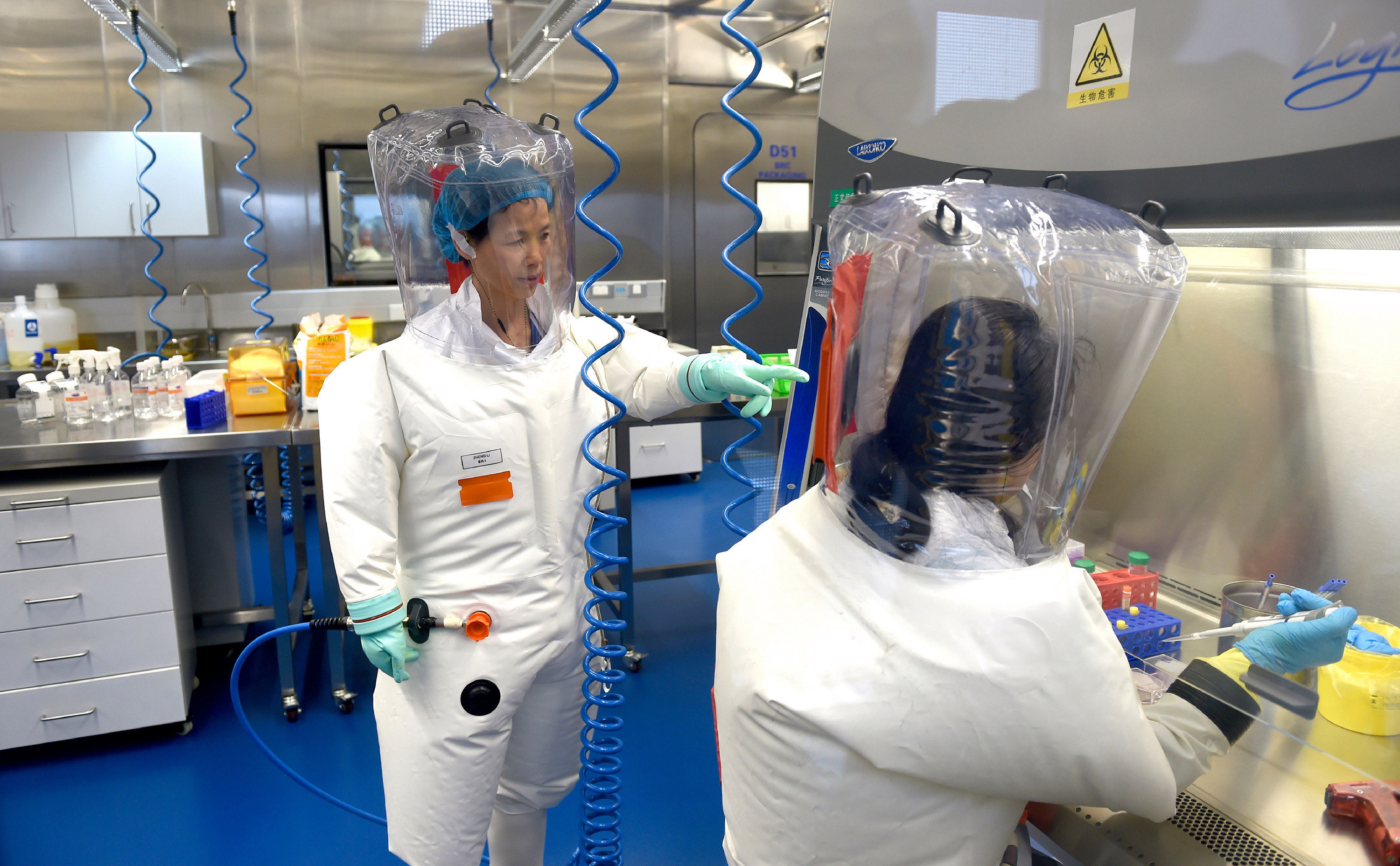
The chief scientist for emerging disease at the Wuhan Institute of Virology, Shi Zhengli, said in an email that the letter’s suspicions were misplaced and would damage the world’s ability to respond to pandemics. “It’s definitely not acceptable,” Shi said of the group’s call to see her lab’s records. “Who can provide an evidence that does not exist?”
“It’s really sad to read this ‘Letter’ written by these 18 prominent scientists.” Shi wrote in her email. “The hypothesis of a lab leaking is just based on the expertise of a lab which has long been working on bat coronaviruses which are phylogenetically related to SARS-CoV-2. This kind of claim will definitely damage the reputation and enthusiasm of scientists who are dedicated to work on the novel animal viruses which have potential spillover risk to human populations and eventually weaken the ability of humans to prevent the next pandemic.”

AP IMAGES
The discussion around the lab leak hypothesis has already become highly political. In the US, it has been embraced most loudly by Republican lawmakers and conservative media figures, including Fox News host Tucker Carlson. The resulting polarization has had a chilling effect on scientists, some of whom have been reluctant to express their own concerns, says Relman.
“We felt motivated to say something because science is not living up to what it can be, which is a very fair and rigorous and open effort to gain greater clarity on something,” he says. “For me, part of the purpose was to create a safe space for other scientists to say something of their own.”
“Ideally, this is a relatively uncontroversial call for being as clear-eyed as possible in testing several viable hypotheses for which we have little data,” says Megan Palmer, a biosecurity expert at Stanford University who is not affiliated with the letter group. “When politics are complex and stakes are high, a reminder from prominent experts may be what is needed to compel careful consideration by others.”